DeepEdge: QoE-based Resource Allocation for Future Heterogeneous and Dynamic Edge-IoT Applications
![]() A research project supported by National Science Foundation as project
CNS-1909520, CNS-2246698.
A research project supported by National Science Foundation as project
CNS-1909520, CNS-2246698.
• Synopsis:
The emerging Internet of Things (IoT) is connecting increasing numbers of smart devices and enabling varieties of heterogeneous IoT applications, empowered by cloud and edge computing technologies. In particular, edge or fog computing technologies will significantly benefit IoT applications that are delay-sensitive, bandwidth/data intensive, or that require closer intelligence. However, for effective Edge-IoT resource allocation, significant challenges exist due to the following requirements and constraints: 1) the demand side that a massive number of IoT devices can run heterogeneous applications with various Quality of Service (QoS) requirements and different priorities; and 2) the supply side that the edge clouds need to dynamically and optimally allocate limited and multidimensional resources (CPU, storage, and bandwidth) at geospatially distributed points. The objective of this project is to respond to these challenges by designing and developing a new Edge-IoT framework named DeepEdge using deep online learning that allocates resources to heterogeneous IoT applications and dynamic IoT devices to maximize users' Quality of Experience (QoE). The proposed research will advance knowledge and fundamentally change the way future edge computing systems work in supporting heterogeneous and dynamic IoT applications. The transformative research outcomes will benefit users and society with inexpensive and effective IoT application delivery, and contribute to important societal challenges in supporting emerging IoT devices and applications. The project will also broadly involve and impact K-12 underrepresented groups and female students in computer science, and develop strong research and education integration for various levels of students.
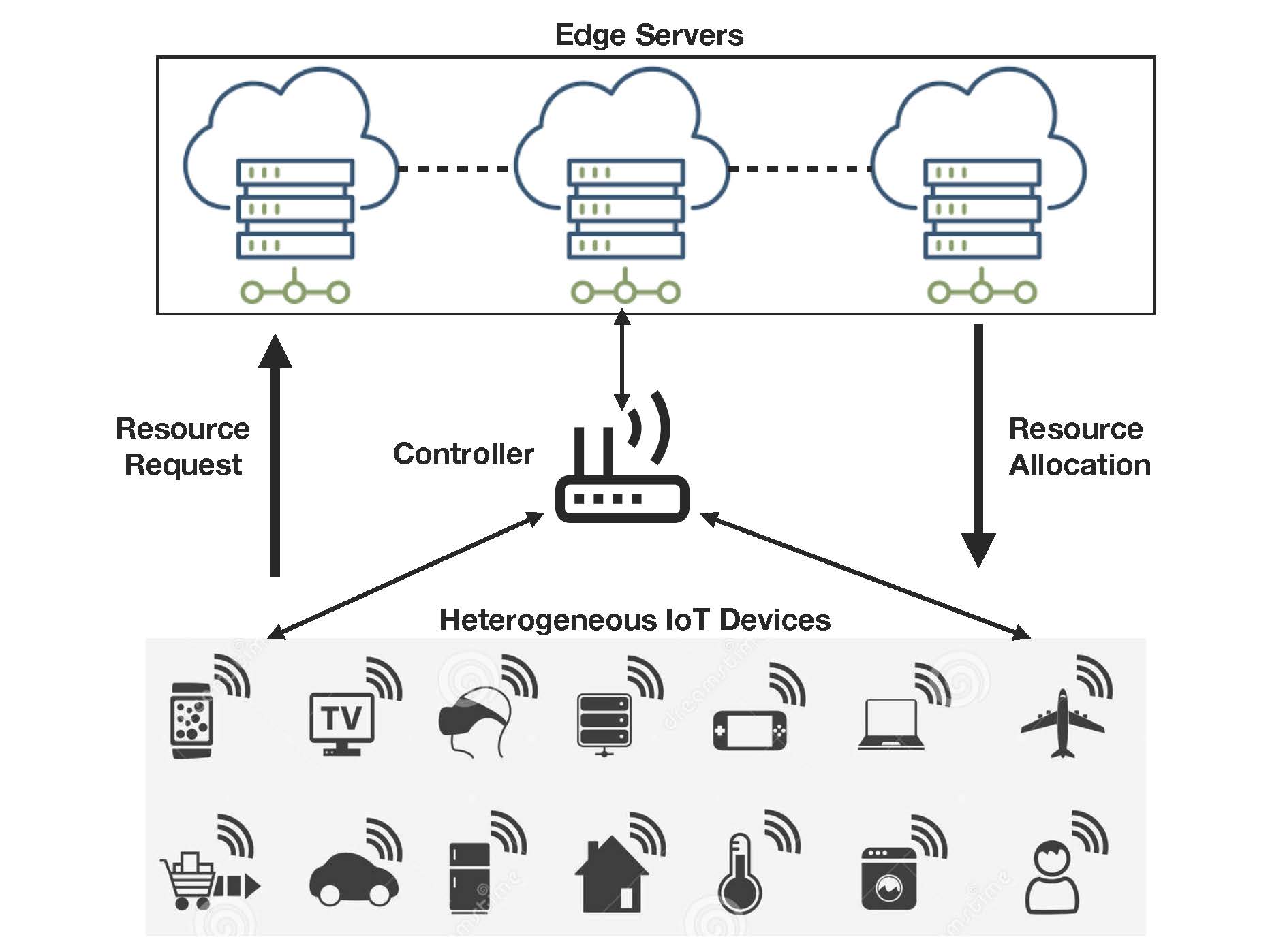
The goal of the proposed research is to develop the framework, model, and algorithms in effectively delivering heterogeneous IoT applications on edge clouds and provisioning high-quality QoE for users. More specifically, the project will result in: i) a new QoE model to quantify the users satisfaction and its related factors including multiple applications QoS requirements and applications priority; ii) a new deep machine learning based two-stage resource allocation scheme that will adapt application QoS requirements according to available resources at the edge cloud and maintain application's priority, and will intelligently and jointly allocate communication and computation resources with the objective of maximization of users QoE; iii) a novel deep Q-learning scheme that will dynamically select the most appropriate edge nodes to handle the multiple application tasks with the goal to optimize the task execution delay; iv) a hardware and software test-bed implementation to validate and evaluate the effectiveness, efficiency, and the practicality of the proposed research.
• Personnel:
 PI: Dr. Jianli Pan
PI: Dr. Jianli Pan
 Post-doc scholar: Dr. Ismail Alqerm
Post-doc scholar: Dr. Ismail Alqerm
• Publications:
• Ismail Alqerm and Jianli Pan, “I-HARF: Intelligent and Hierarchical Framework for Adaptive Resource Facilitation in Edge-IoT Systems,” to appear at IEEE Internet of Things Journal (IOT-J), February 2022. Impact Factor: 9.52.
• Ismail Alqerm and Jianli Pan, “DeepEdge: A New QoE-based Resource Allocation Framework Using Deep Reinforcement Learning for Future Heterogeneous Edge-IoT Applications,” IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management (TNSM), October 2021. Impact Factor: 6.43.
• Ismail Alqerm, Jianyu Wang, Jianli Pan, and Yuanni Liu, “BEHAVE: Behavior-Aware, Intelligent and Fair Resource Management for Heterogeneous Edge-IoT Systems,” IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC), March 2021. Impact Factor: 5.12.
• Jianli Pan, Jianyu Wang, Ismail Alqerm, et.al, “ORCA: Enabling an Owner-centric and Data-driven Management Paradigm for Future Heterogeneous Edge-IoT Systems,” accepted by IEEE Communications Magazine, December 2020. Impact Factor: 10.36.
• Ismail Alqerm and Jianli Pan, “Enhanced Online Q-Learning Scheme for Resource Allocation with Maximum Utility and Fairness in Edge- IoT Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering (TNSE), Vol: 7, Issue: 4, pp 3074-3086, December 2020. Impact Factor: 5.22.
• Educational, Outreach, and Broader Impacts Activities:
• Women in Computing Club
Women C.A.N. (Computers and Networking) (http://www.cs.umsl.edu/~womencan/) is a recently formed organization at the University of Missouri, Saint Louis whose goal is to educate, empower, and encourage women in the field of Computer Science; a field which has seen a drastic decline in the percentage of women over the last several decades. Our members hope to promote the growth of women in Computer Science by: EDUCATING young girls through volunteer activities;
EMPOWERING each other by instilling confidence;
ENCOURAGING women to pursue a Computer Science Career.
• CLIMB (Collaborative Laboratory Internships and Mentoring Blueprint)
The University of Missouri, St. Louis and the Jennings School District have developed a model for how urban universities and urban high schools can work together to begin to reduce the opportunity gap facing disadvantaged underfunded districts. Since 2017, Dr. Pan has been working with Dr. Patricia Parker, the E. Desmond Lee Endowed Professor in Zoological Studies, to work with district administrators to create a paid summer internship program for high-ability but low-opportunity students from Jennings Senior High, a school with a population that is 100% African American and 100% free-lunch-eligible.
Last update 9/29/2022.