What is HTML?
From the small business owner to the student creating a class project, or even casual individuals working on a blog or personal project online, HTML knowledge is incredibly useful. Although the prospect of having to learn a programming language certainly does seem daunting, the good news is that HTML uses common words so that it is fairly simple to pick up.
HTML is Hypertext Markup Language, a format for creating documents and web pages. It was originally invented in the early 1990s by Tim Berners-Lee, and was based on an earlier markup language called SGML (Standard Generalized Markup Language), which was was based on an earlier format simply called GML (Generalized Markup Language) developed at IBM in the 1960s. HTML consists primarily of matching pairs of angle-bracketed tags surrounding human-meaningful text (like this). The tags provide meaning, context, and display information to the text they surround. (WhoIsHostingThis.com)
An easy way to distinguish HTML and CSS from one another is to remember HTML is used for meaning, structure, and content of a webpage and CSS is used for presentation, layout, and design.
Where and How is HTML used?
Almost all webpages utilize or use HTML. It could be said that HTML is the default language of websites. HTML documents are rendered by a a web browser (the application you are using to read this page). HTML rendering hides all the tags, and changes the display of the rest of the content based on what those tags say it should look like.
According to WhoIsHostingThis.com, HTML — Hypertext Markup Language — is the language used for creating web pages and other web-based documents. It consists mainly of matching pairs of angle-bracketed tags, enclosing sections of human-meaningful text. The tags, which are not displayed by web browsers, are used to provide information about how the text and page should be displayed.
The basic structure of an HTML document includes tags, which surround content and apply meaning to it. Below is a screenshot of an HTML document I created, it provides the code to create a basic HTML document/webpage:

What is CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets. It defines the layout, design, and styling of the content and the webpage. CSS is used to do everything from specifying page fonts to describing where to position menu bars and content areas.
The beginner's guide to html highlights and explains some of the advantages of using CSS:
- With CSS we are able to separate content and style as intended.
- We can store all of our styling and presentation information in a separate document, rather than including it in the code of our individual web pages.
- This means that making changes to our style is infinitely easier than it used to be
- Example: Suppose you have a website with 50 pages and you want to change the font used to display the content. With the old methods you would have had to edit every one of those 50 files in order to change one or several lines of code specifying the font. With CSS you just need to alter one file, and the change will filter (or "cascade") through to every single web page.
Writing CSS
All CSS follows the same basic structure, which consists of three parts - the selector, the property and the value:
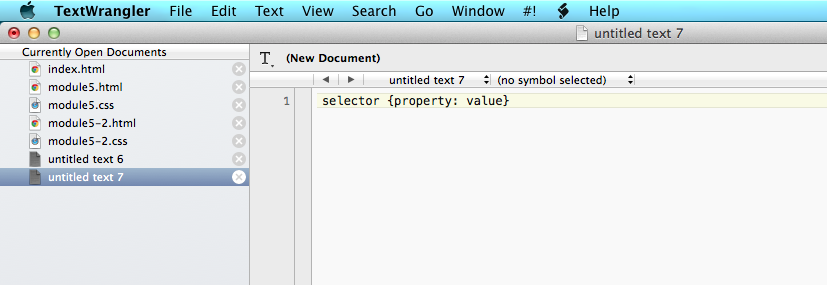
- The selector describes which HTML element we want to add styling to. For example, if we wanted to adjust the styling of our header tag, we would use h1 as our selector.
- The property is the part of the selector we want to add styling to. For example, if we wanted to change our header text to blue, we would use color as our property.
- The value is the part which assigns a particular value to the property that we are changing. Taking the example above, after specifying the h1 selector and the color property, we would assign the value blue. This would style all of our h1 headings in blue.
- Putting all this together, for the above example we would get the following style declaration:
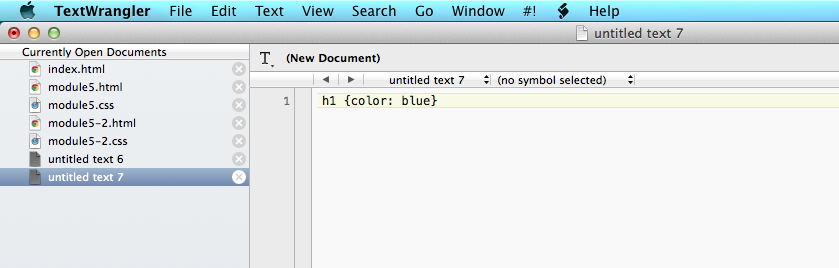
We can apply CSS styling to any of the standard HTML tags, such as body, paragraph, header, etc.
Hopefully by now you have a basic understanding of HTML and CSS, their differences, and their functions. You might think you're ready to start building your own website now. You've answered the important pre-webpage building questions and know the basic structure for both an HTML and CSS document. Well god speed in your web authoring and designing endeavors, the last page provides extra resources to help you with webpage layout and design elements as well as links to additional information on HTML.
