-
What is CSS?
CSS is an acronym for Cascading Style Sheets. While HTML documents describe the framework of elements within a webpace, CSS describes how these HTML elements are visually displayed.
CSS Purpose
Using CSS can save you a lot of work. Rather than adding styling to each individual element in an HTML document, you can modify multiple documents on multiple pages with one sheet.
How to Use CSS
There are three different ways of inserting a style sheet to an HTML document: by using an external style sheet, using an internal style sheet, or by using inline styling.
External Style Sheet
An external style sheet allows you to change the look of an entire website, multiple webpages, with just one .css file. To insert this form of CSS, you must include a metadata < link > element into the < head > section of an HTML document.
Syntax
Place In HTML File
< head > < link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="filename.css" > < /head >Internal Style Sheet
Internal style sheets can be useful if you are trying to apply a unique style to a single page. They are defined within the < style > element inside the < head > section of an HTML page.
Syntax
Place In HTML File
< head > < style > property: value; property: value; < /style > < /head >Inline Style
An inline styling may be used to apply a unique style to a single element in an HTML document. You do this by adding the style attribute straight to the HTML < element tag > of the element you are styling. It can contain any css property.
Syntax
Place In HTML File
< element style="property: value; property: value;"> content < /element >CSS Syntax
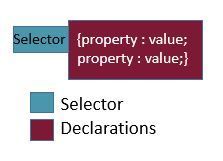
CSS Parts
Name Definition Selector selects what HTML element you want to style Attributes / Styles specific visual changes for different selectors Declaration includes a CSS property name and a value, seperated by a semicolon Property what attribute you are changing Value what you are changing the attribute to
