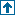



Solve the pseudo-range navigation equations by Gauss-Newton Method Given N known satellite positions and an intial guess of the receiver location, function will approximate receiver position and receiver clock error INPUT: sat - an array of structs, length N; k0 - initial guess of receiver position and clock error; c - speed of light OUTPUT: x,y,z - receiver position; d - receiver clock error function handle of d/dx( F(x,y,z,d) )


0001 % Solve the pseudo-range navigation equations by Gauss-Newton Method 0002 % Given N known satellite positions and an intial guess of the receiver 0003 % location, function will approximate receiver position and receiver clock 0004 % error 0005 % INPUT: sat - an array of structs, length N; k0 - initial guess of 0006 % receiver position and clock error; c - speed of light 0007 % OUTPUT: x,y,z - receiver position; d - receiver clock error 0008 function [x y z d] = solveNavEqns3( sat, k0, c ) 0009 % function handle of d/dx( F(x,y,z,d) ) 0010 rx_k = @(x, sat) 2*(x - sat.x); 0011 % function handle of d/dy( F(x,y,z,d) ) 0012 ry_k = @(y, sat) 2*(y - sat.y); 0013 % function handle of d/dz( F(x,y,z,d) ) 0014 rz_k = @(z, sat) 2*(z - sat.z); 0015 % function handle of d/dd( F(x,y,z,d) ) 0016 rd_k = @(d, sat) 2*c^2*(sat.t - d); 0017 % function handle for pseudo-range navigation function, F(x,y,z,d) 0018 F_k = @(d, sat, dist) dist - (c * (sat.t - d))^2; 0019 % function handle for computing euclidean distance of a satellite to the 0020 % receiver position 0021 euclidean_dist = @(x_k, sat) ... 0022 (x_k(1) - sat.x)^2 + ... 0023 (x_k(2) - sat.y)^2 + ... 0024 (x_k(3) - sat.z)^2; 0025 0026 nsats = length(sat); % number of satellites given 0027 ed = zeros( nsats, 1 ); % array of each satellite distance 0028 DF = zeros( nsats, 4 ); % Jacobian matrix 0029 F = zeros( nsats, 1 ); % vector of solutions to nav. eqns. 0030 % k is our iterative solution of Ax = b 0031 k = k0; 0032 % NOTE: k(1) - x; k(2) - y; k(3) - z; k(4) - d 0033 % we choose an arbitrary number of times to iterate 0034 % (i.e. there is no mechanism to say when the solution is good enough) 0035 for i = 1:20, 0036 % compute and populate distance of each satellite to receiver pos. 0037 for j = 1:nsats, ed(j) = euclidean_dist(k, sat(j)); end 0038 % compute and populate the Jacobian matrix 0039 for j = 1:nsats, 0040 DF(j,:) = [ ... 0041 rx_k(k(1), sat(j)) ... 0042 ry_k(k(2), sat(j)) ... 0043 rz_k(k(3), sat(j)) ... 0044 rd_k(k(4), sat(j)) ]; 0045 end 0046 % compute and populate solution to nav. eqns. 0047 for j = 1:nsats, F(j) = F_k(k(4), sat(j), ed(j)); end 0048 % this is the 'Gauss' part; looks like Least-Squares 0049 % multiply both sides by transpose; (A^T)*A*x = -(A^T)*b 0050 s = (DF' * DF) \ -(DF' * F); 0051 % this is the 'Newton' part; add our solution to the sys. of eqns. to 0052 % our current guess, and get our next best guess 0053 k = k + s; 0054 % RINSE, REPEAT ... 0055 end % END for i 0056 % return the approximated results 0057 x = k(1); 0058 y = k(2); 0059 z = k(3); 0060 d = k(4); 0061 end % END solveNavEqns3