Questions for Chapter 2
BONUS Question
Fill in the blank with the correct organic family name (a bit of pronunciation license here, as well as the course being taught in February) .

[Answer]
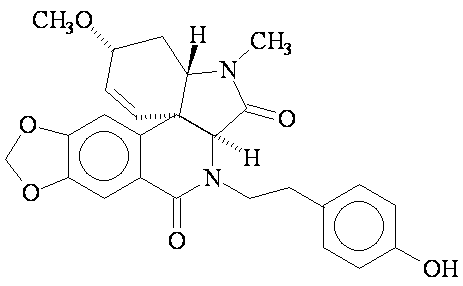
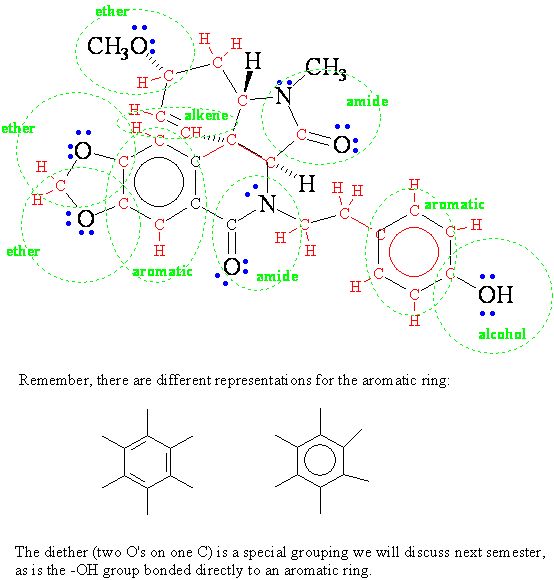
1. The structure shown below is that of plicamine, a recently discovered member of a family of natural products that exhibits a wide range of biological activities.
Answer the following questions about the structure of plicamine:
- How many carbon atoms are there in plicamine?
- Explicitly draw in all hydrogen atoms in the plicamine molecule.
- Explicitly add all non-bonded electrons to atoms in plicamine.
- The name "plicamine" suggests the presence of a particular functional group. However, there is no amine present. What related functional group is present in plicamine?
- Circle all the functional groups in the molecule and name the family of organic compounds to which they belong.
[Answer]
2. The structure of trifluoroacetyl chloride {F3C(C=O)Cl} has a carbonyl group bonded to the Cl and the F3C group. (Or you could look it up on ChemSpider.com)
The partial charges of some of the atoms in the molecule are:
| oxygen | -0.271 | ||
| carbon in carbonyl | +0.326 | ||
| fluorine | -0.162 | ||
| sp3-hybridized carbon | +0.466 | ||
What is the charge on chlorine?
3. Crystals of poppy acid, a component of the latex of opium poppy, have been known since the 19th century to take up (interact with) a wide range of molecules during growth from solution. The variety of functional groups in poppy acid may explain this ability.
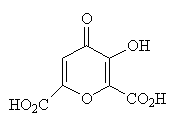
- Circle the functional groups in poppy acid.
- State to which family of organic compounds each functional group belongs.
- Expand the structure of poppy acid to show all atoms and all non-bonding electrons.
- Which parts of poppy acid can act as hydrogen-bond donors?
- As hydrogen-bond acceptors?
- There is at least one opportunity for poppy acid to exhibit intramolecular hydrogen-bonding. Draw the structure of poppy acid that shows the intramolecular hydrogen-bond. [Intra- means "within"; inter- means "between".]
[Answer]
4. This is a question on polarity from the 313 Supplement:
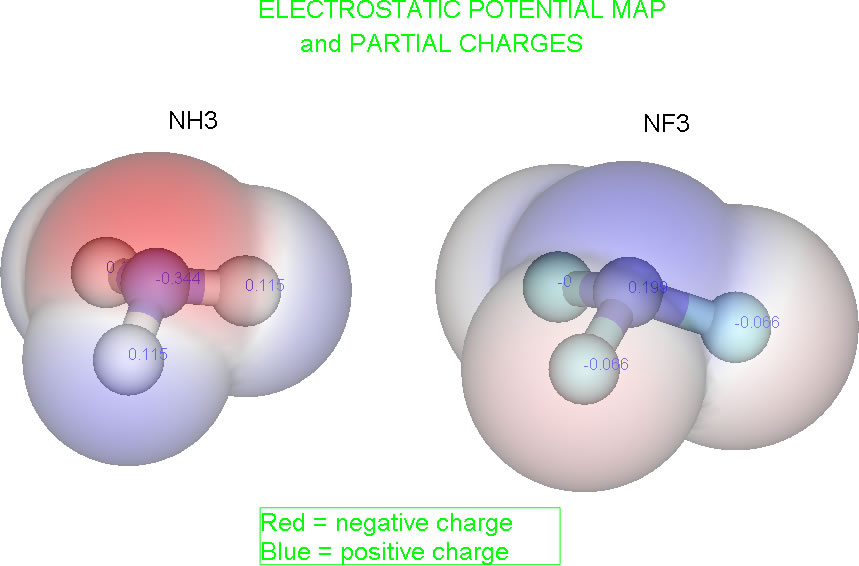
F is more electronegative than H and so the N−F bond dipole should be larger than the N−H bond dipole. However, the molecular dipole moments for :NH3 and :NF3 are 1.47 D and 0.24 D, respectively. Explain. [Hint: the non-bonded electrons are important to the explanation, so draw the correct geometries for the molecules and explicitly determine the direction of the bond dipoles and then the effect of the non-bonded pair.]
While you are working out an answer, here is a graphic of the electrostatic potential maps of the two molecules.
[Answer]
5. What is the charge on the carbon atom in the molecule shown below. Remember to include the proper sign in your numerical answer.
[Answer]
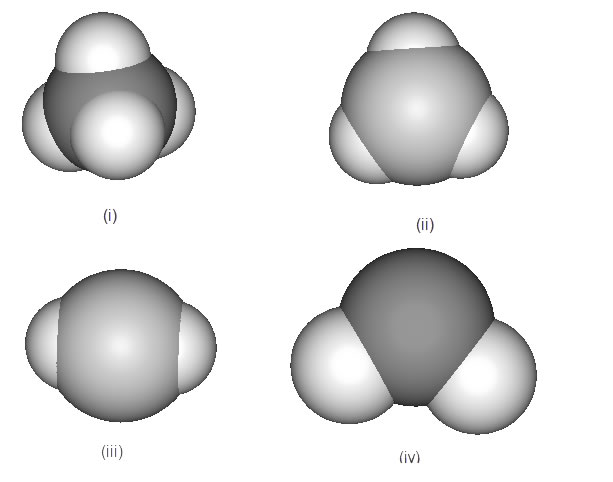
6. Match the following molecular substances with one of the molecular models (i) to (iv) that correctly depicts the geometry of the corresponding molecule. . The lobes can contain either bonding or non-bonding electrons.
a) SeO2 b) BeF2 c) PCl3 d) BBr3 [Answer]
Try the problems from the MIT Open Course site Problem Set 1(#4); 5(#2a). There are answers also.

Nick Uhlig
RedBubble http://www.redbubble.com/people/nickuhlig/portfolio?ref=carousel_portfolio
Plicamine does not have the amine functional group. It does have two amide functional groups, along with several functional group, circled and labeled below.
The molecule is neutral and so the partial charges on all the atoms must total 0.
3F's + 1C(in C=O) + 1C(in CF3) + O + Cl = 0
So: 3(-.162) + .326 + .466 + (-.271) + Cl = 0
+0.035 + Cl = 0
Cl = -0.035
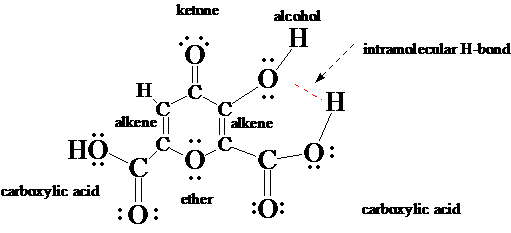
Hydrogen bond donors are the H's on the alcohol and carboxylic acid groups.
Hydrogen bond acceptors are the O's (non-bonded electrons) in the alcohol, carboxylic acid, ketone and ether groups.
Each of these nitrogens has 3 sigma bonds and 1 non-bonded pair of electrons and so 4 molecular orbitals are required to accommodate the 4 electron pairs. Thus, the nitrogen atoms are sp3-hybridized, approximately tetrahedral geometry and ~109 deg. bond angles. Draw the two molecules in their correct geometry -- one good way is shown below.
The electronegativity order of the atoms is F > N > H, so now draw in the bond dipole arrows as shown in the picture. (Vector magnitudes are not drawn to scale.) We might expect the N-F dipoles to be larger than the N-H dipoles (in opposite directions) because the E.N. difference between N-F is larger than the E.N. difference between N-H (you could look at Pauling E.N. numbers to confirm this.)
Next, determine the net dipole for the bonds. The answer is shown and labeled next to each molecule.
If only the bond dipoles were important in the overall dipole moment, then we might expect NF3 to be more polar because of its more polar N-F bonds. But this is not in accord with the facts.
Now, take into account the non-bonding pair on each N. There is a large amount of electron density in the sp3 non-bonded pair orbitals on each nitrogen.
For the NF3 molecule, the direction of the non-bonded pair occupancy is opposite the direction of the three N-F dipoles. These withdrawals of electron density from N, being in opposite directions, will partiall cancel out, leaving a very small net dipole. It is impossible to say in which direction the net dipole points. It would depend on which is greater: the sum of the three N-F dipoles or the N-: "dipole". It is impossible to say without further experiment. (The esp map above shows the net dipole pointing toward the F's.)
For the NH3 molecule, the direction of the non-bonded pair occupancy is the same as the direction of the three N-H dipoles. Therefore, the electron donation to N from H's, and the electron withdrawal from N by the non-bonded pair are in the same direction and add to each other. This leads to a larger net dipole moment in the direction shown.
5. Observe that this molecule has an overall -1 charge. So after the C's charge is determined, all the atomic charges must add to -1. You could write this equation: 3(.072)+(-1.340)+x = -1. The charge on C is +.124
6. For each molecule, the number of valence electrons on the central atom must be determined. Then the other atoms must be placed in the correct connectivity and any non-bonding electrons on the central atom must be shown. (The non-bonding electrons on the attached atoms won't be shown as they do not determine the geometry.)
a) Se is Grp VI, has 6 valence electrons and is bonded to each O atom by a double bond and there is one non-bonded pair on Se. O=Se=O
2sigma + 1 nb pair is trigonal planar geometry (ii)
b) Be is Grp 2 and has 2 valence electrons. One electron from Be forms each of the two sigma bonds with the F atoms F-Be-F.
2 sigms is linear geometry (iii)
c) P is Grp V and will resemble N. It can be sp3, with 3 bonds to Cl's, and a non-bonded pair in an sp3 orbital. :PCl3.
So tetrahedral geometry (i)
d) B is Grp III and uses sp2 hybrid orbitals to form 3 bonds to Br's. Trigonal planar geometry (ii)