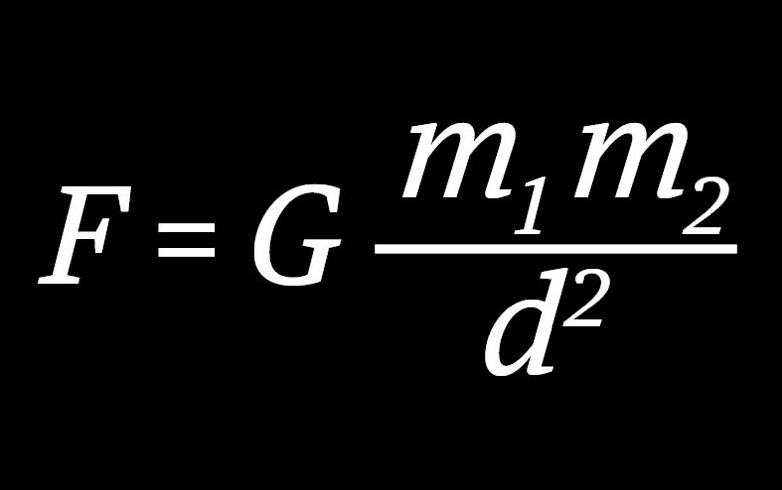PROJECT C: Celestial Mechanics
Intro: We can use orbital mechanics to simulate motions of an object orbiting the Earth, or any other body within our solar
system and galaxy. NASA uses celestial mechanics to model trajectories of satellites, space ships/stations (ISS, Tiangong 1) , and for
geocentric and geosynchronous orbital telescopes (Hubble Tele., Fermi Gamma-Ray Space Tele.).
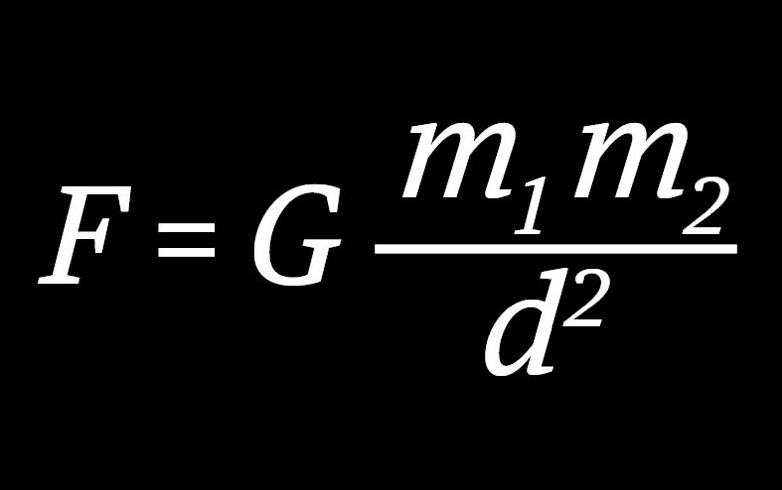
From the above equation; known as the Law of Universal Graitation, we have that when two masses graviational interact, they
attract each other with forces of equal magnitude. D is the distance between the mass centers and G = 6.67 x
10-11
Nm2/kg2; known as the gravitational constant.
Step 1 (Computer Problem 6.3.9 Pg. 319)
Step 2 (Computer Problem 6.3.10 Pg. 319)
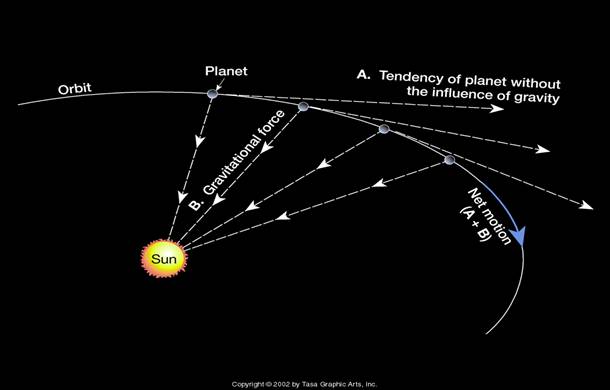
He we are comparing the initial conditions of the masses m1 and m2.
Step 3 (Computer Problem 6.3.11 Pg. 314 [New Version])
|